11.03.2024
The Power of Hydrogen: A Closer Look at the Essential Uses of Hydrogen in Industrial Applications
In the ever-evolving landscape of sustainable energy, Green hydrogen has emerged as an important element in the quest for a cleaner and more efficient future and That caught the attention of professionals at the forefront of companies who aim to reduce their CO2 emissions. But do you know what are the uses of hydrogen in different industries?
Green hydrogen production is at the forefront of the transition to a more sustainable energy landscape. Green hydrogen refers to hydrogen produced using renewable energy sources, such as wind, solar, or hydropower, and is considered one of the cleanest forms of energy available. Unlike grey hydrogen, which is produced from natural gas or other sources with significant carbon emissions, green hydrogen production does not contribute to greenhouse gas emissions when executed correctly.
One of the key uses of green hydrogen is its potential to replace grey hydrogen from industrial processes where hydrogen is unavoidable and irreplaceable, such as fertilizer production, desulphurisation, chemical feedstock and many others. Green Hydrogen can also be used to store excess renewable energy produced in photovoltaic plants and wind farms. In periods of low energy demand, surplus electricity can be used to electrolyze water, separating it into hydrogen and oxygen. This hydrogen can then be stored for later use in various applications, such as fuel cells or industrial processes, effectively acting as an energy carrier and grid-balancing tool.

This article aims to shed light on the various uses of hydrogen, offering insights that can support your decision-making process on whether to adopt hydrogen in your industry. We will explore the industries that rely on hydrogen and explore the diverse applications that make it a game-changer in the energy transition.
Hydrogen: The Universal Energy Carrier
Hydrogen, the lightest and most abundant element in the universe, holds immense promise as a versatile energy carrier. It can be produced through various methods that you can explore in our article: Green Hydrogen Production: A Sustainable Energy Game-Changer.
By producing hydrogen on-site, you can facilitate the conversion of electricity and water into hydrogen and oxygen, offering a clean and efficient energy solution for various applications and industrial sectors, including steelmaking, glass and ceramics, concrete production, steelmaking, fertilizers, Transportation Sector, Aerospace Industry, Refining Industry and many others. But what truly matters are the uses of hydrogen and how it transforms diverse industries.
The uses of hydrogen: A Glimpse into Industrial Applications
Chemical Industry
Hydrogen's journey into the chemical industry has been nothing short of transformative. It serves as a vital feedstock for a multitude of chemical processes, particularly in the production of ammonia and methanol. These compounds are building blocks for numerous chemical products, from fertilizers to plastics. Without the production of ammonia, all of the available land mass in the world could only yield enough food for only half of the current world population. Among the several uses of hydrogen, this versatile element also facilitates the desulfurization of conventional fossil fuels, ensuring cleaner and more environmentally friendly end products.
Transportation Sector
Hydrogen is heralded as a green alternative to fossil fuels in the transportation sector. Fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) powered by hydrogen have gained traction due to their zero-emission profiles and fast refuelling capabilities compared to battery technology. Hydrogen fueling stations have started appearing across the globe, making it an attractive option for the automotive industry. Whether for cars, buses, or trucks, hydrogen holds the promise of a cleaner, more sustainable future for transportation.
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace sector benefits from hydrogen's high energy density and lightweight. It is a propellant of choice for some rockets and space shuttles, enabling missions into outer space. There are many uses of Hydrogen in space exploration. It is vital, to ensure safe and efficient sources of energy for travel beyond our planet.
Energy Storage
One of the most well-known uses of hydrogen is in energy storage, contributing to grid stability and renewable energy integration. Through a process known as Power-to-Gas (P2G), surplus electricity, often generated from renewable sources, is used to produce hydrogen. This hydrogen can be stored and later converted back into electricity, serving as a crucial element in managing the intermittency of renewable energy sources.
Steel Manufacturing
The steel industry is one of the largest industrial sources of greenhouse gas emissions. Hydrogen is poised to revolutionize this sector by replacing traditional approaches in the iron ore reduction process. The use of hydrogen as a reducing agent significantly reduces carbon emissions, making steel production more environmentally friendly. What’s more, the final end product possesses higher purity and better quality compared to steel produced using fossil fuels. Hydrogen is also utilised to produce wolfram from ores and the same process can be used to produce copper or other metals.
Electronics and Semiconductor Industry
In the electronics and semiconductor industry hydrogen is used for processing high-purity silicon and other materials. It is an essential component in chemical vapor deposition processes, ensuring the quality and precision of electronic components. These electronic components are virtually in every computer, phone, smart device or other modern electronics.
Food and Beverage Industry
The uses of hydrogen in the food industry are various, hydrogen is employed in the hydrogenation of edible oils, which converts unsaturated fats into saturated fats, thereby improving the stability and shelf life of food products. If you have eaten peanut butter recently, then it is highly likely it included hydrogenated oil as an additive. Hydrogen also finds application in the production of margarine, baked goods, and snacks.
Power Generation
One of the uses of Hydrogen is for power generation. Gas turbines and fuel cells can efficiently convert hydrogen into electricity, offering a clean and flexible energy source. It's particularly valuable in areas where grid access is limited, as it enables off-grid power generation. Compared to power generators fueled by diesel, hydrogen power generators are quiet, clean and smaller for the same power.
Heat and Heating Applications
Hydrogen can be utilized for high-temperature heating in industrial processes, including metal annealing and glass manufacturing. Its combustion produces heat with minimal environmental impact, reducing the carbon footprint of such operations. Hydrogen also leaves no residue upon combustion, leaving less residue on products.
Healthcare Sector
Hydrogen's applications in the healthcare sector are diverse. It is used for sterilization purposes in hospitals and laboratories. Additionally, hydrogen-rich water is being explored for its potential health benefits as an antioxidant.
Refining Industry
In the oil refining industry, hydrogen is essential for removing impurities from crude oil and improving the quality of end products such as gasoline and diesel. It enhances the efficiency of refining processes and reduces environmental emissions.
Horticulture and Agriculture
Hydrogen can be employed in controlled environment agriculture for enriching greenhouse atmospheres. This enhances plant growth and increases crop yields, offering a sustainable solution for food production.
The Role of Electrolyser Stacks
As you just saw, the uses of hydrogen are diverse, and you might have guessed that electrolyser stack manufacturing companies have an important role in enabling the widespread adoption of hydrogen in these industries. Electrolyser stacks are at the heart of the hydrogen production process and are expected to have the following characteristics:
Efficiency: Electrolyser stacks need to operate at high efficiency to minimize energy losses during hydrogen production. A well-designed stack ensures that more of the input energy is converted into hydrogen, making the overall process more cost-effective.
Reliability: Reliability is a critical factor, especially in industries where downtime can lead to substantial financial losses. Stacks must be engineered to withstand the rigours of continuous operation, with minimal maintenance requirements.
Scalability: Many industries require hydrogen in varying quantities. The ability to scale up or down the hydrogen production capacity by adding or removing stacks is a key consideration, enabling your customers to meet their specific demands.
Stargate's Alkaline electrolyser stack for system integrators. Learn more about Stargate's Alkaline Stack:
- Alkaline electrolyser stacks
- From 20 to 100 Nm3/h
- Performance Guarantee
- Engineering support
- Innovative in-house design
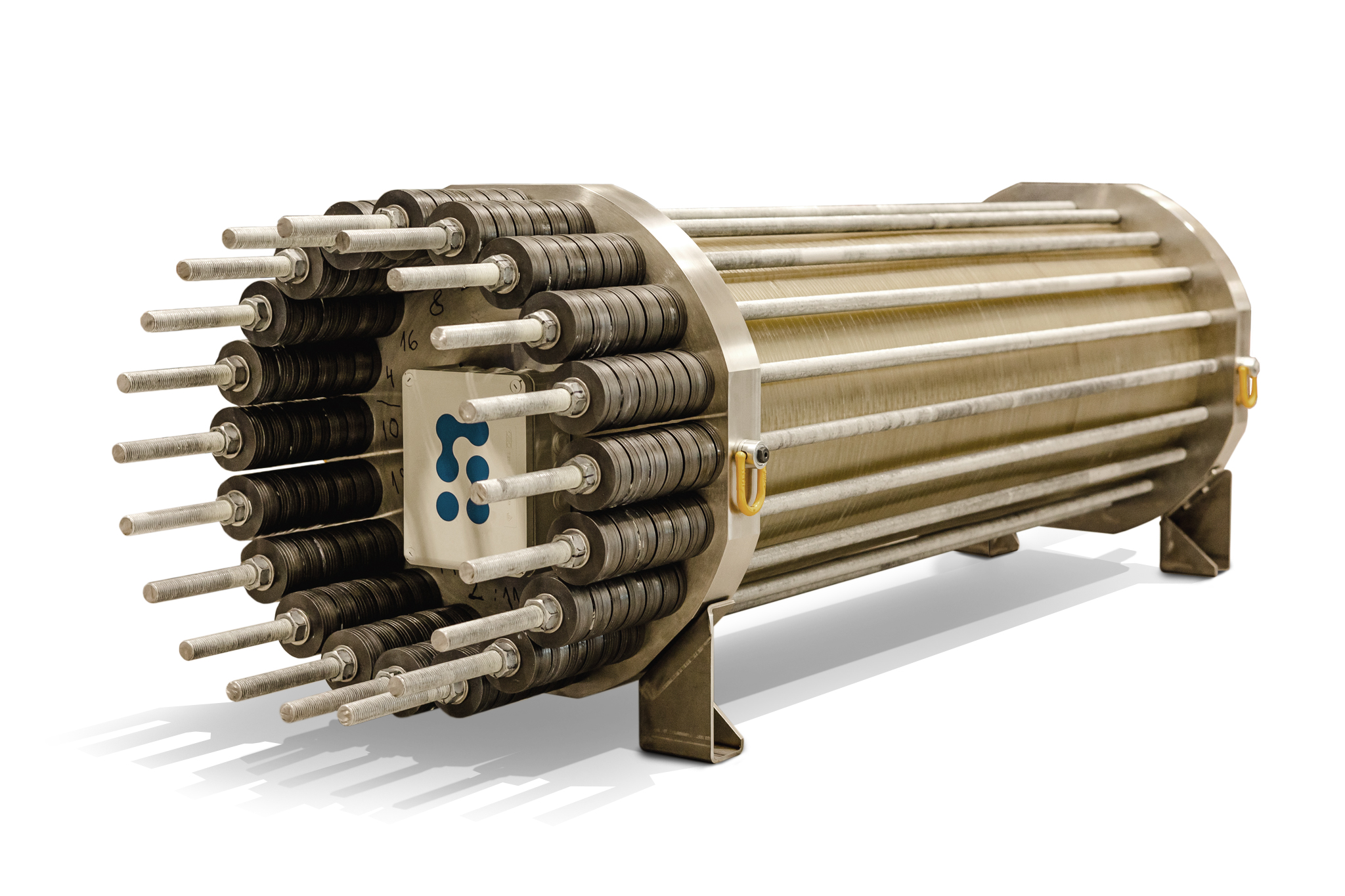

Our pressurised alkaline electrolyser stacks are available with a 6-month lead time and come with a performance guarantee. The stacks have a proven track record of long operational lifespans, which makes them a reliable choice for continuous hydrogen production. This durability minimizes downtime and maintenance costs, contributing to the economic feasibility of green hydrogen. The technology has been validated by several institutions including the Fraunhofer Institute. The stacks come in a wide range of sizes, operate at 32 bar and are customisable for the best product-market fit. We provide engineering support to help you get started.
The Road Ahead: How Stargate Hydrogen enables the industry of tomorrow.
Just as stacks are the heart of an Electrolyser, Research and Development is the heart of Stargate Hydrogen. R&D is vital for staying competitive in the hydrogen market, which is why we are collaborating with academic institutions, research organizations, and industry experts to advance stack technologies. Exploring materials, designs, and manufacturing processes that can enhance stack performance and durability.
The uses of hydrogen as an energy carrier are undeniable, and its applications across many industries are evidence of its transformative potential. By offering efficient, reliable, and scalable stack solutions, you can empower industries to embrace the hydrogen potential, reduce carbon emissions, and drive a cleaner, more sustainable future. The journey has just begun, and the possibilities are boundless. Embrace the power of hydrogen, and together, we can shape a greener tomorrow.
